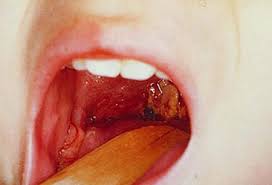
Pharyngitis is a sudden painful inflammation of the pharynx, the back portion of the throat that includes the posterior third of the tongue, soft palate, and tonsils. It is commonly referred as a sore throat. It is the most common infection and inflammation of the respiratory tract. The incidence of Pharyngitis peaks during winter and early spring in regions that have warm summers and cold winters because of environmental exposure to viral agents and poorly ventilated rooms. Viral pharyngitis spreads easily in the droplets of coughs and sneezes and unclean hands that have been exposed to the contaminated fluids.
Chronic pharyngitis is a persistent inflammation of the pharynx. It is common in adults who work in dusty surroundings, abuse of voice such as stage performer or singer, suffer from a chronic cough, or habitually use alcohol and tobacco. There are three types of chronic pharyngitis:
- Hypertrophic: It is characterized by general thickening and congestion of the pharyngeal mucous membrane.
- Atrophic: It is probably a late stage of the first type (the membrane is thin, whitish, glistening and at times wrinkled)
- Chronic granular (Clergyman’s sore throat): It is characterized by numerous swollen lymph follicles on the pharyngeal wall.