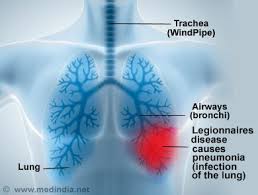
The legionella bacterium also causes Pontiac fever, a milder illness resembling the flu. Separately or together, the two illnesses are sometimes called legionellosis. Pontiac fever usually clears on its own, but untreated legionnaires’ disease can be fatal. Although prompt treatment with antibiotics usually cures legionnaires’ disease, some people continue to experience problems after treatment.
Symptoms:
Legionnaires’ disease usually develops two to 10 days after exposure to legionella bacteria. It frequently begins with the following signs and symptoms:
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Chills
- Fever that may be 104 F (40 C) or higher
By the second or third day, you’ll develop other signs and symptoms that may include:
- Cough, which may bring up mucus and sometimes blood
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
- Confusion or other mental changes
Although legionnaires’ disease primarily affects the lungs, it occasionally can cause infections in wounds and in other parts of the body, including the heart.
A mild form of legionnaires’ disease — known as Pontiac fever — may produce signs and symptoms including a fever, chills, headache and muscle aches. Pontiac fever doesn’t infect your lungs, and symptoms usually clear within two to five days.