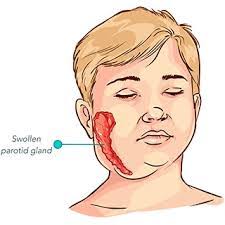
Mupms is a viral disease characterized by salivary gland swelling.It occurs primarily in childhood.
Transmission:
Mumps virus is transmitted via respiratory droplets.The virus infects upper respiratory tract and then spreads through the blood to infect the salivary glands,especially parotid gland,testes,ovaries, pancreas and in some cases meninges.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of mumps normally appear 2-3 weeks after the patient has been infected. However, almost 20 percent of people with the virus do not suffer any symptoms at all.
Initially, flu-like symptoms will appear, such as:
- Body aches
- Headache
- Loss of appetite and/or nausea
- General fatigue
- Fever(low-grade)
Over the next few days, the classic symptoms of mumps will develop. The main symptom is painful and swollen parotid glands, one of three sets of salivary glands; this causes the person’s cheeks to puff out. The swelling normally does not occur in one go – it happens in waves.
Other associated symptoms can include:
- Pain in the sides of the face where it is swollen.
- Pain experienced when swallowing.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Fever (up to 103 degrees Fahrenheit).
- A dry mouth
- Pain in joints.
Rarely, adults can contract mumps. In these cases, the symptoms are generally the same, but sometimes slightly worse and complications are slightly more likely.
Complications:
- Orchitis(mostly unilateral)
- Meningitis (usually benign,self-limited)
- Parotitis