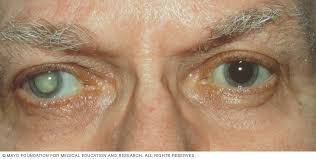
Risk factors for Cataract
A number of factors can increase your risk of developing cataracts, including:
- Older age
- Family history of cataracts
- Greater exposure to sunlight
- Living at a higher altitude
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- History of eye injury, inflammation, or surgery
- Radiation treatments on your upper body
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol in excess
- Long-term use of corticosteroid drugs (1,5,6)
While most cataracts are related to aging, some people are born with cataracts or develop them during childhood. These are known as congenital cataracts.
Sometimes congenital cataracts have genetic causes, or they may be due to trauma or infection in the uterus. Conditions that can cause them include:
- Myotonic dystrophy, a type of muscular dystrophy
- Galactosemia, a rare metabolic disorder
- Neurofibromatosis type 2, a disorder in which tumors grow on nerves
- Rubella, sometimes called German measles
- Toxoplasmosis, a parasitic infection
- Cytomegalovirus, a viral infection
- Syphilis
- Herpes simplex virus
Congenital cataracts don’t always affect your vision, but if they do, they’re usually treated with surgery soon after they’re diagnosed.
Other Eye Conditions That Affect Your Vision
- Color Blindness Hyperopia (Farsightedness) Myopia (Nearsightedness) Presbyopia (Age-Related Vision Changes)
Types of Cataracts Based on Cause and Location
Cataracts can be broadly divided into four groups based on their causes:
- Age-Related Cataracts This group accounts for the large majority of cataracts.
- Congenital Cataracts Cataracts in babies and children can be caused by a number of different factors
- Secondary Cataracts In adults, cataracts can be caused by diseases like diabetes, or by drugs, such as corticosteroids.
- Traumatic Cataracts An injury to one or both eyes may result in cataracts. This can happen soon after the injury or several years later.
Cataracts can also be categorized based on the area of the lens they affect. There are three types of cataracts, based on location:
- Nuclear Cataracts This type of cataract affects the center of your lens. It tends to cause yellowing and clouding of the area.
- Cortical Cataracts This type of cataract affects the edges of your lens. It tends to cause white marks and streaks that gradually extend to the center of your lens.
- Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts This type of cataract affects the back of your lens. It tends to cause an initially small opaque area in the path of your vision, and often progresses faster than other types of cataracts.
Symptoms of Cataracts
The most common initial symptom of a cataract is a small area of blurred vision. Over time, this area of blurred vision is likely to grow as your lens becomes more clouded. Eventually, you may get the sense that your overall vision is dull or blurry.