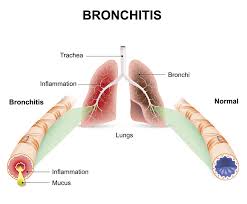
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, those being the air passages that extend from the windpipe into the lungs.
The inflammation may be caused by a
- virus,
- bacteria,
- smoking
- or the inhalation of chemical pollutants or dust.
When the cells of the bronchial–lining tissue are irritated beyond a certain point, the tiny hairs (cilia) within them, which normally trap and eliminate pollutants, stop functioning. Consequently, the air passages become clogged by debris and mucous and irritation increases. In response, a heavy secretion of mucus develops, which causes the characteristic cough of bronchitis. It may be either acute or chronic. Bronchitis often follows a common cold or any infection of the nose and throat.
Types:
There are two basic types of bronchitis:-
- Acute bronchitis – This lasts for 2 to 4 weeks and is usually responsive to therapy
- Chronic bronchitis – This is a different entity and leads to long term damage to the inner walls of the airways in the lungs. This is part of a group of lung diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD. This is a progressively worsening condition that cannot be cured.
Symptoms:
The symptoms are;
- A frequent cough
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Wheezing and noisy breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain accompanying coughing and deep breathing
- Fever with chills and body ache
- Sore throat
- Stuffy or runny nose with or without stuffy sinuses and headache