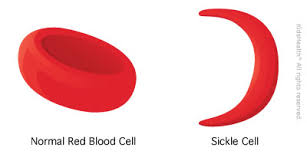
Sickle cell anemia is a blood disease that affects red blood cells. Normal red blood cells are round. In people with sickle cell anemia, hemoglobin (a substance in red blood cells) becomes defective and causes the red blood cells to change shape. The faulty hemoglobin is called hemoglobin S, (HgbS) and it replaces normal hemoglobin called: hemoglobin A (HgbA). Over time, the red blood cells become rigid and shaped like crescent moons or sickles.
Sign and symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of sickle cell disease usually begin in early childhood. Characteristic features of this disorder include a low number of red blood cells, repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain. The severity of symptoms varies from person to person. Some people have mild symptoms, while others are frequently hospitalized for more serious complications.
Although sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed in infancy, if you or your child develops any of the following problems, see your doctor right away or seek emergency medical care:
- Unexplained episodes of severe pain, such as pain in the abdomen, chest, bones or joints.
- Swelling in the hands or feet.
- Abdominal swelling, especially if the area is tender to the touch.
- Fever. People with sickle cell anemia have an increased risk of infection, and fever can be the first sign of an infection.
- Pale skin or nail beds.
- Yellow tint to the skin or whites of the eyes.
Signs or symptoms of stroke. If you notice one-sided paralysis or weakness in the face, arms or legs; confusion; trouble walking or talking; sudden vision problems or unexplained numbness; or a headache, it is an emergency situation.