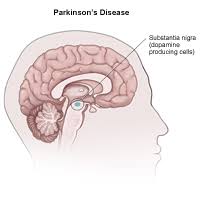
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing (“dopaminergic”) neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra.
In the early stages of Parkinson’s disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk. Your speech may become soft or slurred. Parkinson’s disease symptoms worsen as your condition progresses over time.
What are the four primary symptoms of PD?
The following are the most common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- Muscle rigidity. Stiffness when the arm, leg, or neck is moved back and forth.
- Resting tremor. Tremor (involuntary movement from contracting muscles) that is most prominent at rest.
- Bradykinesia. Slowness in initiating movement.
- Postural instability. Poor posture and balance that may cause falls; gait or balance problems.
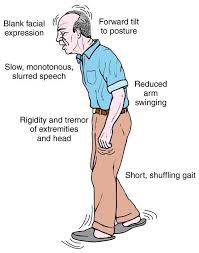
Other symptoms are divided into motor (movement-related) and nonmotor symptoms.
Motor symptoms:
- Tremor
- Bradykinesia (slow movement)
- Rigidity and freezing in place
- Stooped posture
- Shuffling gait
- Decreased arm swing when walking
- Difficulty rising from a chair
- Micrographia (small, cramped handwriting)
- Lack of facial expression
- Slowed activities of daily living (for example, eating, dressing, and bathing)
- Difficulty turning in bed
- Remaining in a certain position for a long period of time
Nonmotor symptoms
- Diminished sense of smell
- Low voice volume (hypophonia)
- Difficulty speaking (dysarthria)
- Painful foot cramps
- Sleep disturbance
- Depression
- Emotional changes (fearful and insecure)
- Skin problems
- Constipation
- Drooling
- Increased sweating
- Urinary frequency/urgency
- Male erectile dysfunction