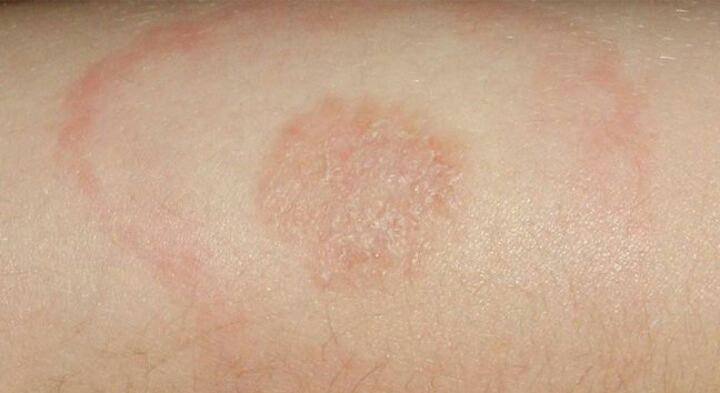
Lyme disease is best treated in the early stages. Early treatment is a simple 14 to 21 day course of oral antibiotics to eliminate all traces of infection. Medications used to treat Lyme disease include:
- Amoxicillin for adults, younger children, and women who are nursing or breastfeeding
- doxycycline for adults and children older than 8 years old
Persistent or chronic Lyme disease is treated with intravenous antibiotics for a period of 14 to 21 days. Though this treatment eliminates the infection, your symptoms improve more slowly.
It’s unknown why symptoms, like joint pain, continue after the bacteria have been destroyed. Some doctors believe that persistent symptoms occur in people who are prone to autoimmune disease.
Lyme disease prevention mostly involves decreasing your risk of experiencing a tick bite. Take the following steps to prevent tick bites:
- Wear full clothes when in the outdoors.
- Make your yard unfriendly to ticks by clearing wooded areas, keeping underbrush to a minimum, and putting woodpiles in areas with lots of sun.
- Use insect repellent. Insect repellent with 10% DEET will protect you for a period of about two hours. Don’t use more DEET than what is required for the time you’ll be outside, and don’t use DEET on the hands of young children or on the faces of children less than 2 months old.oil of lemon gives the same protection as DEET when used in similar concentrations. It shouldn’t be used on children under the age of 3.
- Be vigilant. Check your children, pets, and yourself for ticks. Don’t assume you can’t be infected again; people can get Lyme disease more than once.
- Remove ticks with tweezers. Apply the tweezers near the head or the mouth and pull gently. Check to be certain that all tick parts have been removed. Contact your doctor whenever a tick bites you or your loved ones.