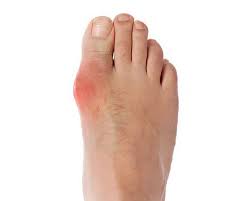
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritischaracterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot, and swollen joint. Pain typically comes on rapidly in less than twelve hours.The joint at the base of the big toe is affected in about half of cases.It may also result intophi, kidney stones, or urate nephropathy.
What Are The Stages of Gout?
There are several stages of gout:
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia is the period prior to the first gout attack. There are no symptoms, but blood uric acid levels are high and crystals are forming in the joint.
Acute gout, or a gout attack, happens when something (such as a night of drinking) causes uric acid levels to spike or jostles the crystals that have formed in a joint, triggering the attack. The resulting inflammation and pain usually strike at night and intensify over the next eight to 12 hours. The symptoms ease after a few days and likely go away in a week to 10 days. Some people never experience a second attack, but an estimated 60% of people who have a gout attack will have a second one within a year. Overall, 84% may have another attack within three years.
Interval gout is the time between attacks. Although there’s no pain, the gout isn’t gone. Low-level inflammation may be damaging joints. This is the time to begin managing gout – via lifestyle changes and medication – to prevent future attacks or chronic gout.
Chronic gout develops in people with gout whose uric acid levels remain high over a number of years. Attacks become more frequent and the pain may not go away as it used to. Joint damage may occur, which can lead to a loss of mobility. With proper management and treatment, this stage is preventable.

Who Is Affected?
Gout occurs in about 4% of American adults – about 6 million men and 2 million women.
Gout Risk Factors
Genes: If family members have gout, you’re more likely to develop it.
Other health conditions: High cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes and heart disease may raise your risk.
Medications: Diuretic medications or “water pills” taken for high blood pressure can raise uric acid levels; so can some drugs that suppress the immune system taken by rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis patients, as well as transplant recipients.
Gender and age: Gout is more common in men than women until around age 60. Experts believe natural estrogen protects women up to that point.
Diet: Eating red meat and shellfish increases your risk.
Alcohol: For most people, more than two liquor drinks or two beers a day can increase the risk of gout.
Sodas: The fructose in sweet sodas has recently been shown to increase gout risk.
Obesity: Obese people are at a higher risk for gout, and they tend to develop it at a younger age than people of normal weight.